Introduction:
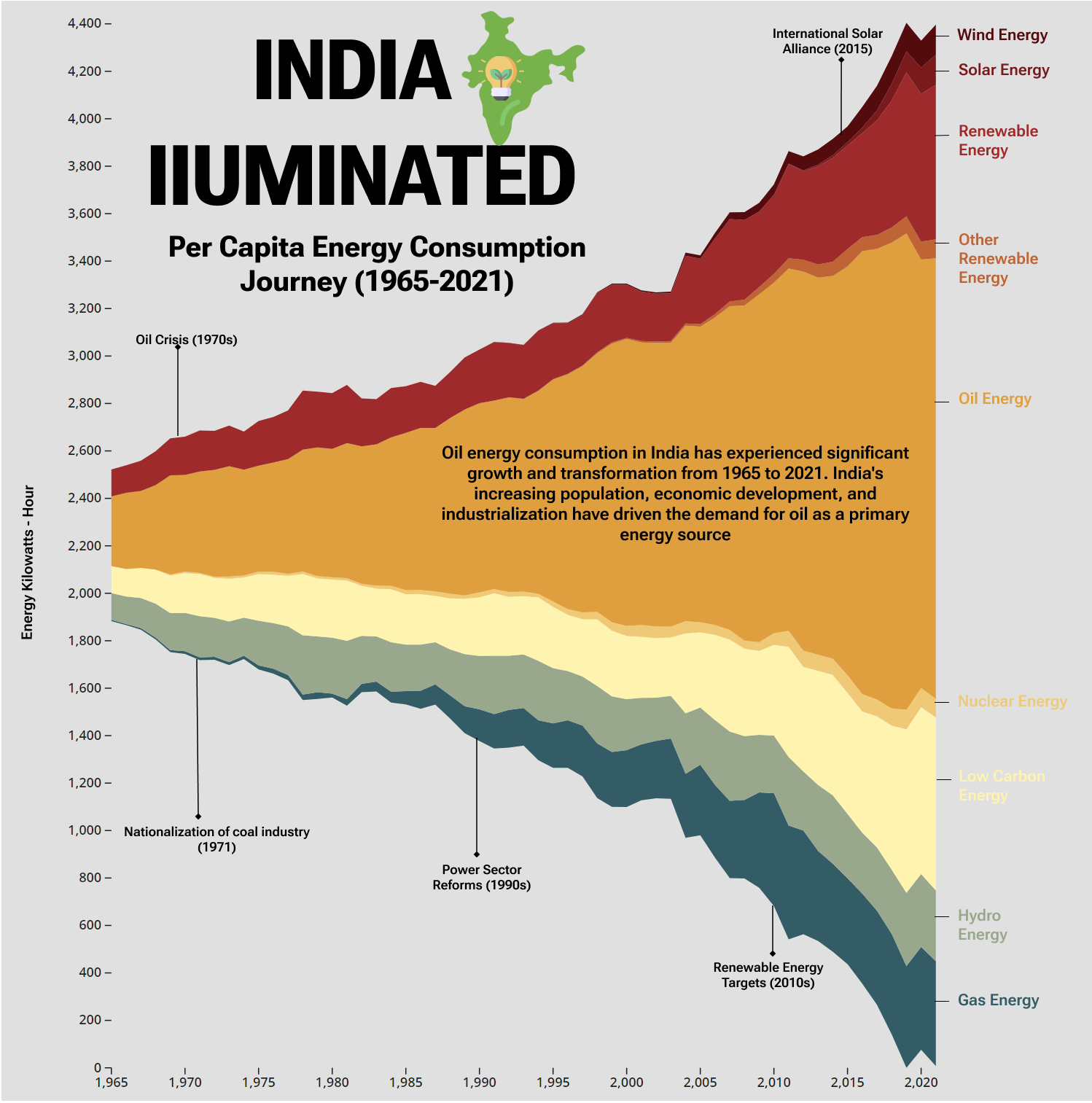
India, a land of diversity and dynamism, has witnessed a remarkable journey in its energy consumption patterns over the past five decades. From the early years of heavy reliance on traditional biomass fuels to the recent surge in renewable energy adoption, India’s energy landscape has undergone significant transformations. In this blog post, we delve into India’s energy consumption journey from 1965 to 2021, exploring the milestones, challenges, and remarkable progress achieved along the way.
The Era of Traditional Biomass (1965-1980):
In the mid-1960s, India predominantly relied on traditional biomass fuels, such as firewood, crop residues, and animal dung, for cooking and heating needs. Electricity consumption was limited, and access to grid-based power was a luxury, particularly in rural areas. As the population grew, so did the energy demand, paving the way for a shift in India’s energy paradigm.
Expansion of Electricity and Fossil Fuel Dependency (1980-2000):
During this phase, India placed significant emphasis on expanding its electricity infrastructure. Thermal power generation, primarily fueled by coal, gained momentum to meet the growing demand. Hydroelectric power projects also played a crucial role, capitalizing on India’s rivers and water resources. Additionally, the use of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) witnessed a rise, gradually replacing traditional biomass fuels in many households.
Diversification and Economic Liberalization (2000-2010):
As India embraced economic liberalization and witnessed rapid industrialization, the diversification of its energy mix became imperative. The focus shifted towards harnessing cleaner energy sources and promoting energy efficiency. Renewable energy gained prominence, with wind and solar power projects being initiated across the country. Natural gas emerged as a cleaner alternative for power generation and transportation, contributing to the diversification efforts.
Renewable Energy Revolution (2010-2021):
The last decade marked a turning point in India’s energy consumption journey, with a strong focus on renewable energy expansion. The government set ambitious targets to increase the share of renewable energy in the country’s power mix. Initiatives like the Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission accelerated solar power capacity addition, leading to a significant rise in solar installations. Wind power also witnessed substantial growth during this period.
Simultaneously, efforts were made to enhance energy efficiency, reduce energy waste, and promote clean cooking solutions. The government launched programs like the Ujwal DISCOM Assurance Yojana (UDAY) to address issues in the power sector and drive sustainable energy consumption practices.
Conclusion:
India’s energy consumption journey from 1965 to 2021 showcases a remarkable shift towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. From a heavy dependence on traditional biomass fuels to the expansion of electricity access and the rapid adoption of renewable energy, India has made significant strides in its pursuit of a greener and more energy-efficient future. As the nation continues to grapple with the challenges of growing energy demands and environmental sustainability, the path carved over the years serves as an inspiration for other countries and a testament to India’s commitment to power progress while preserving the planet for future generations.